Ozone is also a greenhouse gas, but it differs from other greenhouse gases in several ways The effects of ozone depend on its altitude, or where the gas is located vertically in the atmosphere Most ozone naturally exists in the layer of the atmosphere called the stratosphere, which ranges from approximately 6 to 30 miles above the Earth'sAnd the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases is continuing to increase Of the total amount of greenhouse gasses emitted, carbon dioxide covers 76% of the entire volume of gasses hence it is the highest volume of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere Methane It is an attractive fuel found on the ground and the sea floor, but when it escapes to the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane

Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Definition And Effect Medicsky
Which would increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Which would increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere-Water vapor is the most potent of the greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and it's sort of a unique player among the greenhouse gases The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere cannot, in general, be directly modified by human behavior—it's set by air temperatures The warmer the surface, the greater the evaporation rate of waterThe amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today far exceeds the natural range seen over the last 650,000 years Most of the carbon dioxide that people put into the atmosphere comes from burning fossil fuel s such as oil, coal, and natural gas Cars, trucks, trains, and




Global Warming
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,Without its atmosphere and the greenhouse effect, the average temperature at the surface of the Earth would be zero degrees Fahrenheit However, too many greenhouse gases can cause the temperature to increase out of control Such is the case on Venus where greenhouse gases are abundant and the average temperature at the surface is more than 855
Here is why If the atmosphere contains too much of these gases, the whole Earth becomes a hotter and hotter greenhouse The atmosphere holds onto too much of the heat at night instead of letting it escape into space Then, the next day, the Sun heats Earth's surface even more If the atmosphere works too well as a greenhouse, each day gets a The link between greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and warming temperatures is clear CO 2 is continuously exchanged between the land, the air, and the ocean While more than half of emitted CO 2 is removed from the atmosphere through natural processes within a century, about percent remains in the atmosphere for many millennia Since the Industrial Revolution began in the 1700s, people have added a substantial amount of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels, cutting down forests, and conducting other activities (see the US and Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions indicators) When greenhouse gases are emitted into the atmosphere, many remain there
The effect of greenhouse gases There are five gases of human origin that contribute most – together up to 95% of the total – to the increase in global warming Here you will discover the source of their emission, the time they spend in the atmosphere and what percentage they contribute to the greenhouse effectGoing from the level of carbon dioxide in the air before the industrial revolution, 280 parts per million by volume (280 ppm) to twice that, 560 ppm, and letting the climate come into balance will warm the surface by about 3 C How much more carbon dioxide must be added to the atmosphere to warm the surface by another 3 C?Sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) is an extremely potent greenhouse gas SF 6 is very persistent, with an atmospheric lifetime of more than a thousand years Thus, a relatively small amount of SF 6 can have a significant longterm impact on global climate change SF 6 is humanmade, and the primary user of SF 6 is the electric power industry Because of its inertness and dielectric properties, it is




Co2 Emissions Declines From Lockdowns Will Not Solve The Climate Crisis



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
Greenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards space Step 4 Some of this heat is trapped by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm enough toGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warmingThe effect of each greenhouse gas on Earth's climate depends on its chemical nature and its relative concentration in the atmosphereSome gases have a high capacity for absorbing infrared radiation or occur in significant quantities, whereas others have considerably lower capacities for absorption or occur only in trace amounts




25 Wonderful Ways To Reduce Greenhouse Gases Conserve Energy Future



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
Atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it the amount of CO2 might trigger glacial advances and retreats GS Callendar in 1938 solved a set of equations linkingThe approximate mass of all water substances in the atmosphere is 129×10 18 grams The amount of carbon dioxide is 3×10 18 grams These figures are converted into mole by dividing by the molecular weight in grams The molecular weight of H 2Untitled Most important human activities emit greenhouse gases (GHGs) Emissions started to rise dramatically in the 1800s due to the Industrial Revolution and changes in land use Many greenhousegasemitting activities are now essential to the global economy and a fundamental part of modern life Carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
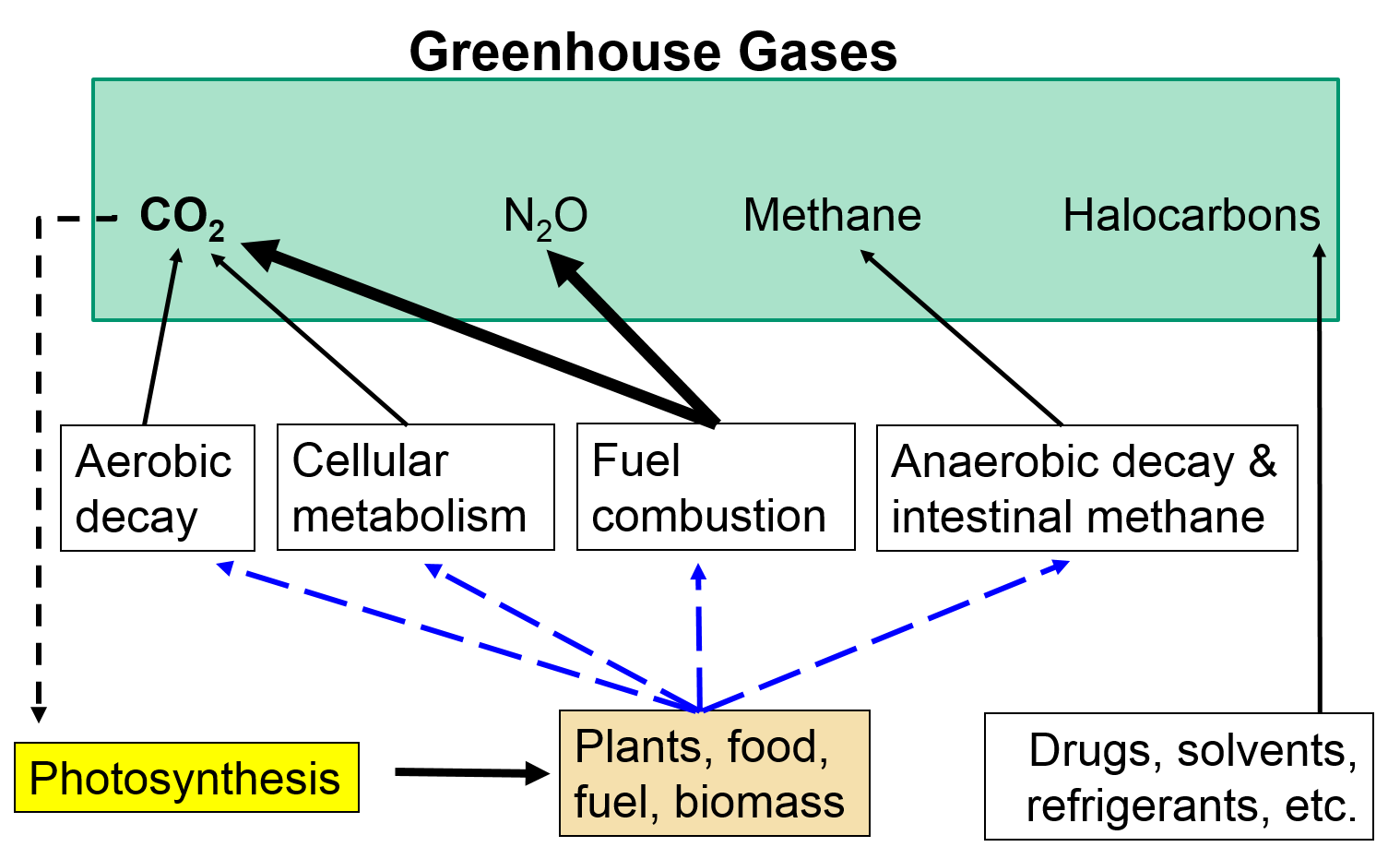



Greenhouse Gases Climate Change
Adding more greenhouse gases decreases the amount of infrared radiation energy leaving the atmosphere To get the energy back in balance, the surface of the Earth has to warm up, so that it will emit more infrared energy, some of which will leave the atmosphere and compensate for the effect of the added greenhouse gasesThe answer lies in the greenhouse effect — gases in our atmosphere (including CO 2, CH 4 (methane) and H 2 O water vapor) trap much of the emitted heat and then reradiate it back to Earth's surface This means that the energy leaving our planet from the top of the atmosphere is less than one would expect given the known temperature of our As concerning as the growing amount of greenhouse gases is the increasing rate at which concentrations are rising In the first 0 years following the Industrial Revolution (), the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increased



1



How Much Of The Heat That Gets Trapped By Greenhouse Gases Is Absorbed By The Ocean Where Does The Rest Go Quora
But the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has skyrocketed to detrimental levels in recent history Related Carbon dioxide soars to record breaking levels not seen in at least 800,000 years Caption This chart from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 11 report shows the relative importance of different factors in driving climate change — through their influence on the atmosphere's radiative forcing, an index of the amount of incoming heat from the sun that is absorbed by the Earth rather than radiated back out into space Measurements of greenhouse gases (GHGs), whether performed in the atmosphere, or over terrestrial or marine ecosystems, have led to a fundamental understanding of the Earth System during the last century Nevertheless, we still do not fully understand global greenhouse gas cycling




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
Greenhouse Gases and Temperature A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surfaceThe table below gives approximate values of gases in the atmosphere for 413 ppm of CO 2 in dry air (this is roughly the average amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere in the middle of the year ) All species have been expressed as ppm, turning 7809% nitrogen into 780,900 ppmGreenhouses gases are atmospheric gases such as carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and water vapor (H 2 O) that absorb and reradiate heat, which warms the lower atmosphere and Earth's surfaceThis process of absorption and reradiation of heat is called the greenhouse effectAlthough greenhouse gases only make up a small percentage of the atmosphere, small changes in the amount



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science
The gases that make up Earth's atmosphere are mostly nitrogen and oxygen, and small quantities of trace gases such as argon, neon, helium, the protective ozone layer, and various greenhouseHuman activities and the greenhouse effect Human activities are increasing the amount of some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere For example farming cattle releases methaneSource EPA's Climate Change Indicators (16) Scientists have carefully examined all this evidence and made a startling discovery There's more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere now than at any other time in at least 650,000 years!




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
Greenhouse gases occur naturally and allow us to survive on Earth by warming air near Earth's surface Human activities are now increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which leads to changes in climate These changes areThe greenhouse effect is not a bad thing Without it, our planet would be too cold for life as we know it But if the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere changes, the strength of the greenhouse effect changes too This is the cause of humanmade climate change by adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, we are trapping more heat Record high levels of greenhouse gas pollution continued to increase the heat trapped in the atmosphere in 19, according to an annual analysis released by NOAA scientists NOAA's Annual Greenhouse Gas Index tracks the concentrations of greenhouse gases being added to the atmosphere principally from humancaused emissions The AGGI then calculates the heat being added to Earth's atmosphere




Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Definition And Effect Medicsky




Global Warming
This imbalance between greenhouse gas emissions and the ability for natural processes to absorb those emissions has resulted in a continued increase in atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere have increased by about 40% since the mid1800s Today's atmosphere absorbs more than 3 watts of incoming solar energy over each square meter of Earth's surface According to NOAA's 19 Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (right axis), the combined heating influence of all major greenhouse gases has increased by 45% relative to 1990 Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRLCarbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas you hear people talk about the most That's because we produce more carbon dioxide than any other greenhouse gas, and it's responsible for most of the warming Some greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for only a short time, but others can stay in the atmosphere and affect the climate for thousands of years




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From
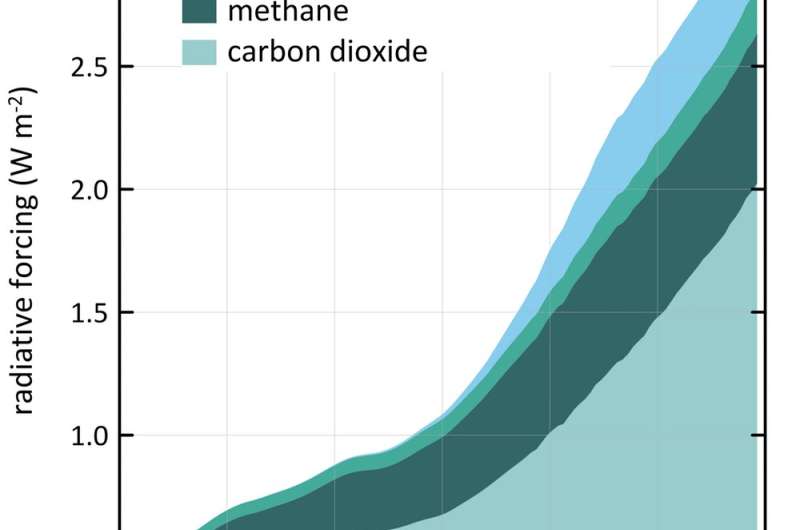



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised
During 17, NOAA's Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network Measurements showed that concentrations of CO 2 in the atmosphere rose by 23 parts per million, following record increases of 29 ppm in 16 and 15 This is the sixth consecutive year CO 2 rose by 2 The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides The carbon cycle's sinks and sources help to regulate the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Besides CO 2 there are other greenhouse gases These include water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Without any greenhouse gases, Earth would be an icy wasteland Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by
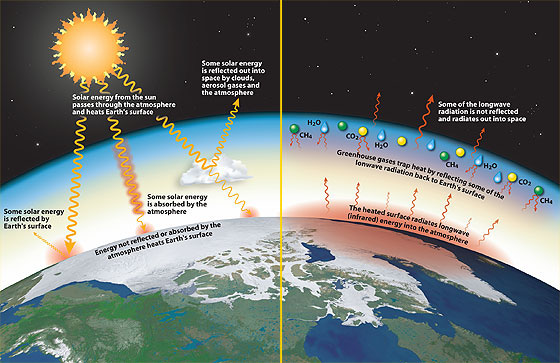



Too Much Of A Good Thing
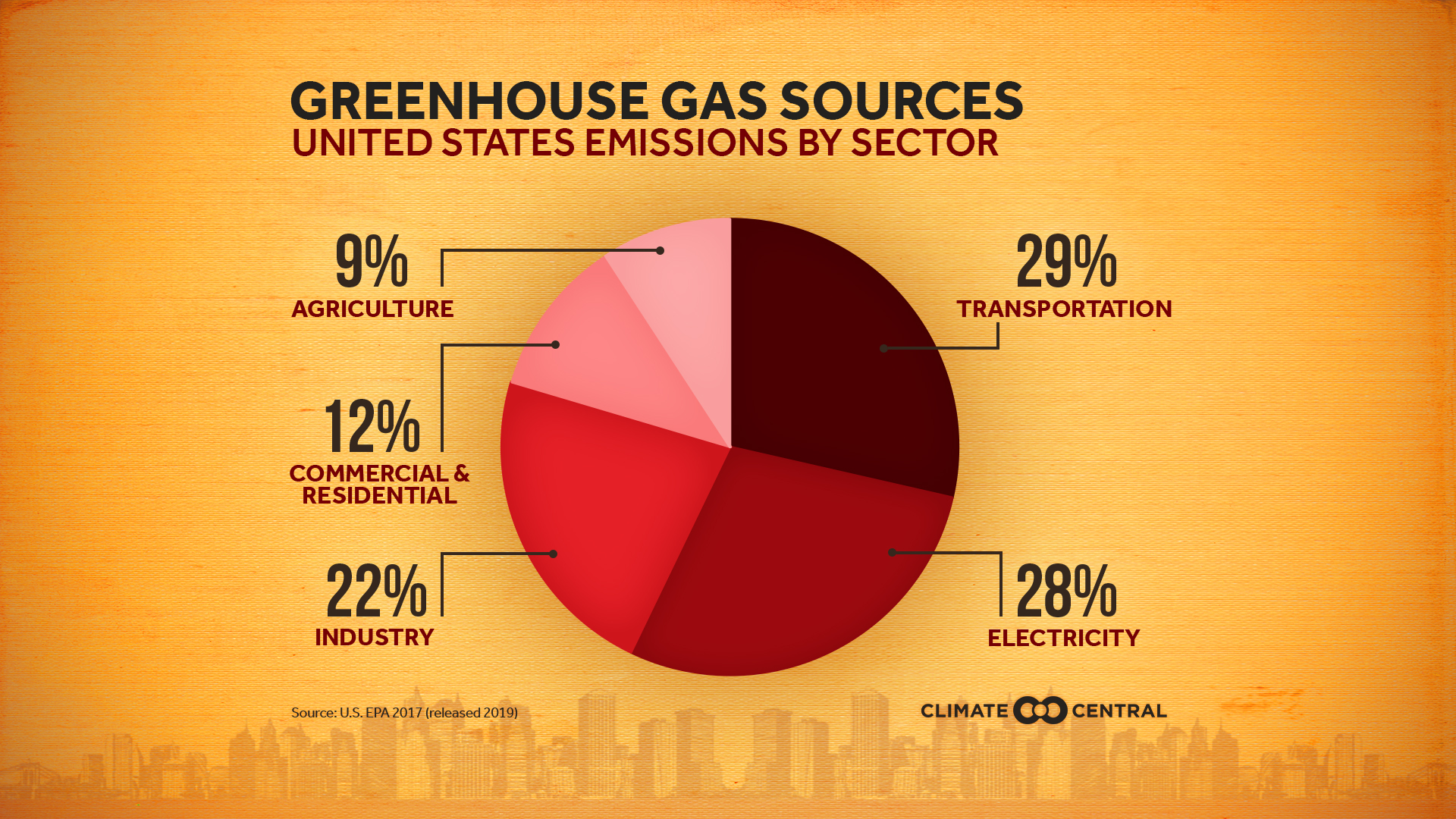



Emissions Sources Climate Central
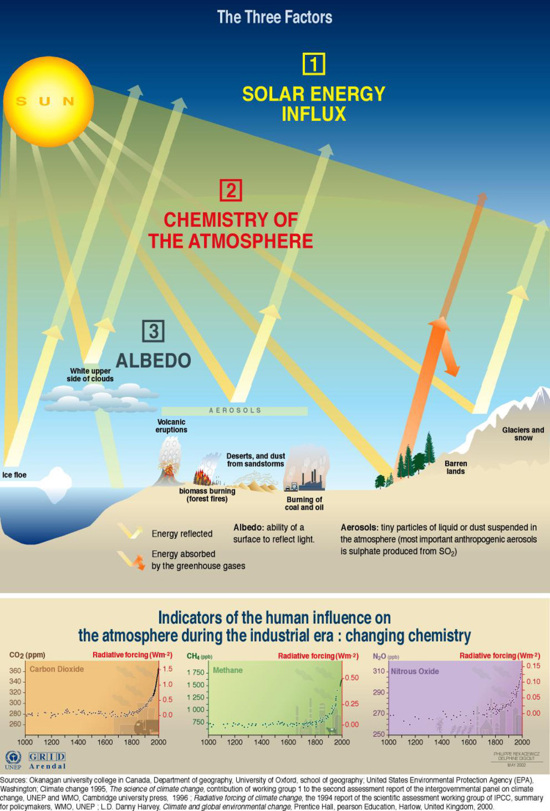



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist
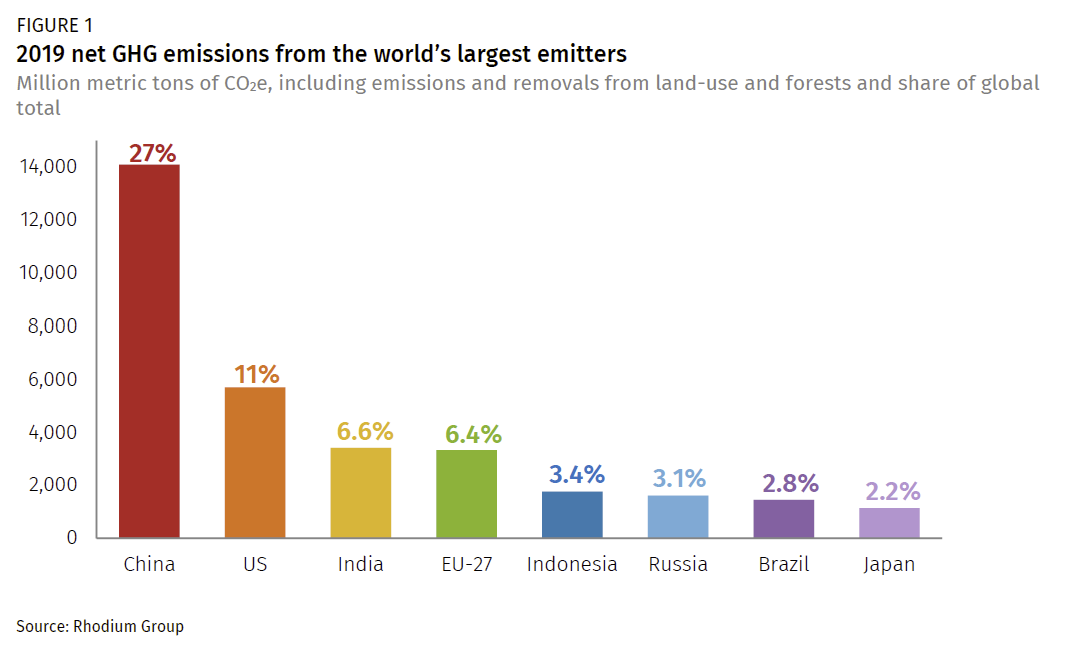



China S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Exceeded The Developed World For The First Time In 19 Rhodium Group



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram




Noaa Global Monitoring Laboratory The Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Aggi



State Of The Climate Bureau Of Meteorology




Eia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview
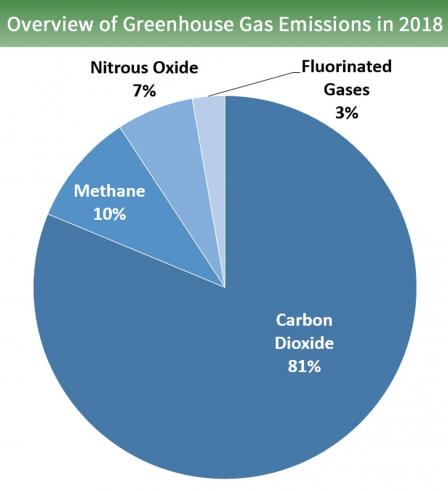



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Percentage Share Of Greenhouse Gases In The Earth Atmosphere 5 Download Scientific Diagram




Sea Level Rise Greenhouse Gas Global Warming Sea Angle Atmosphere Triangle Png Pngwing




Climate Chronicles Chapter 1 Climate Science For The Rest Of Us Ans Conservation Blog



State Of The Climate Bureau Of Meteorology



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Contributions Of Natural Systems And Human Activity To Greenhouse Gas Emissions Sciencedirect




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
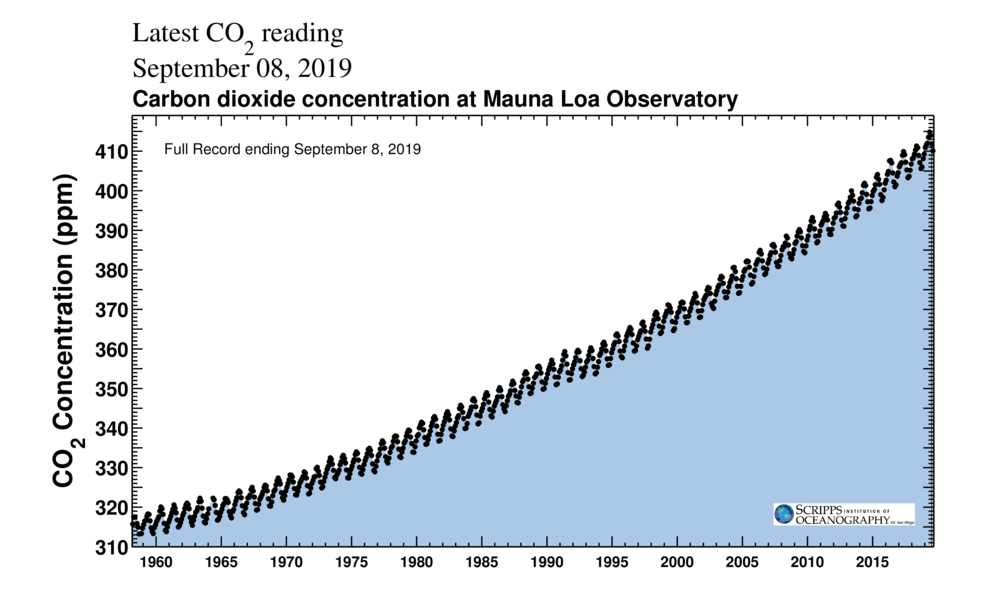



Climate Explained Why Carbon Dioxide Has Such Outsized Influence On Earth S Climate



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Hit New High Un
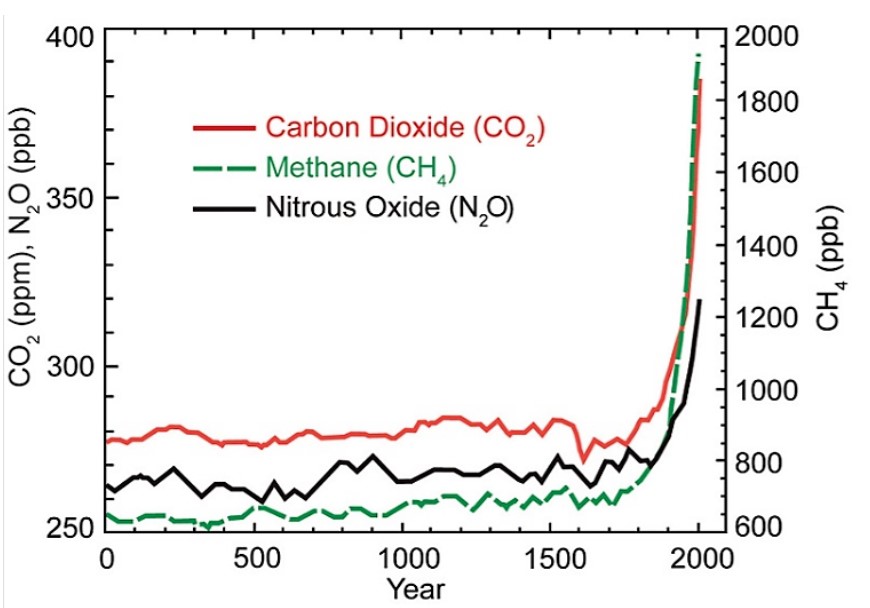



13 11 Carbon Dioxide And Climate Change Chemistry Libretexts




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



1




What Is Nitrous Oxide And Why Is It A Climate Threat Inside Climate News



The Greenhouse Effect
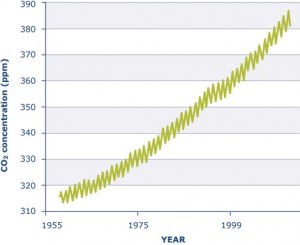



Lakes Climate Change Lake Scientist



The Greenhouse Effect




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




Greenhouse Gases What Is Warming Up Our Earth



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




Greenhouse Gases Viztopia



Why Do We Need Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Quora
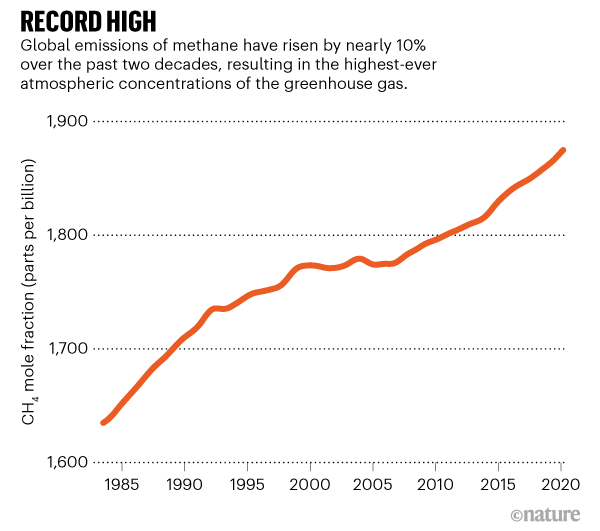



Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
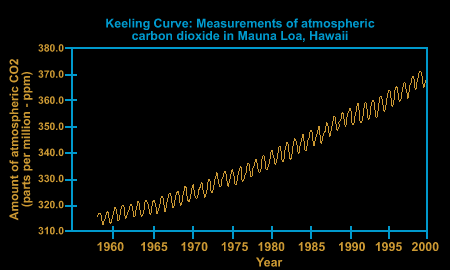



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
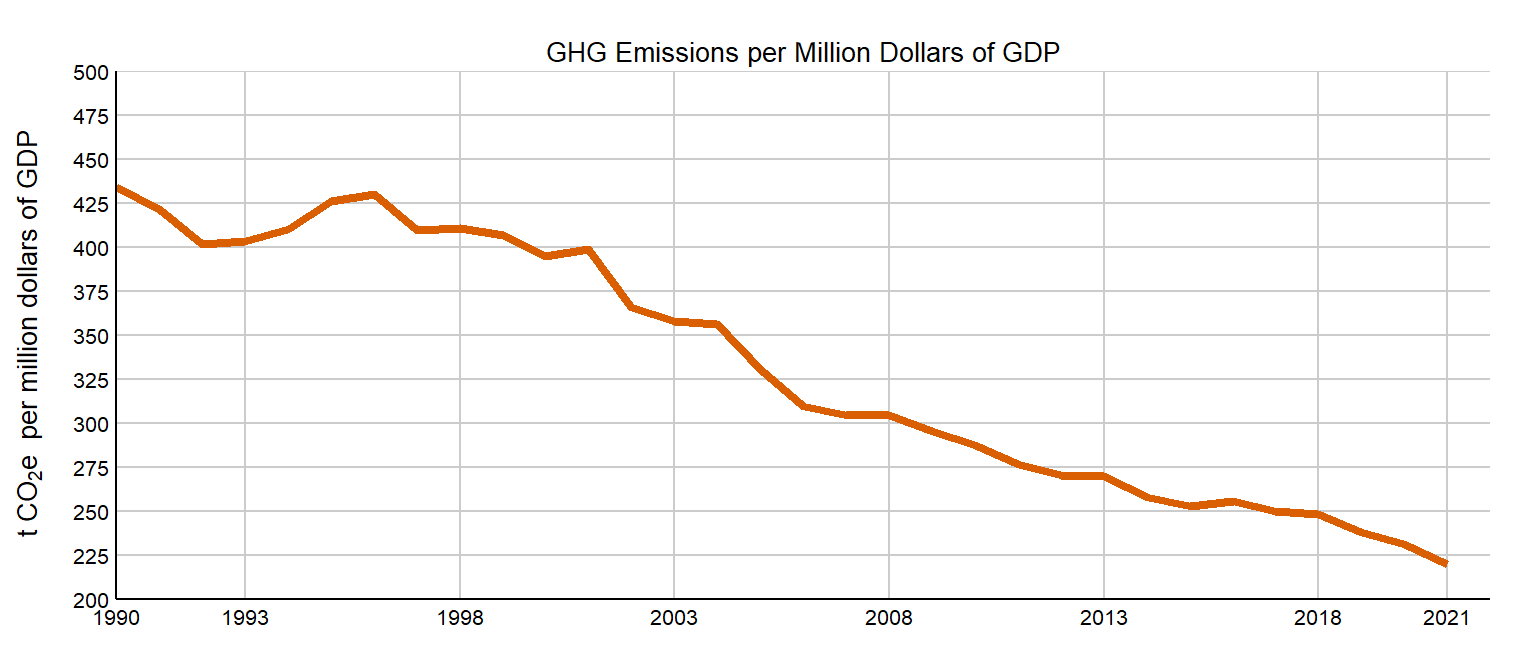



Ghg Emissions Environmental Reporting




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Greenhouse Gas Amounts In Atmosphere Hit Record High Explained News The Indian Express
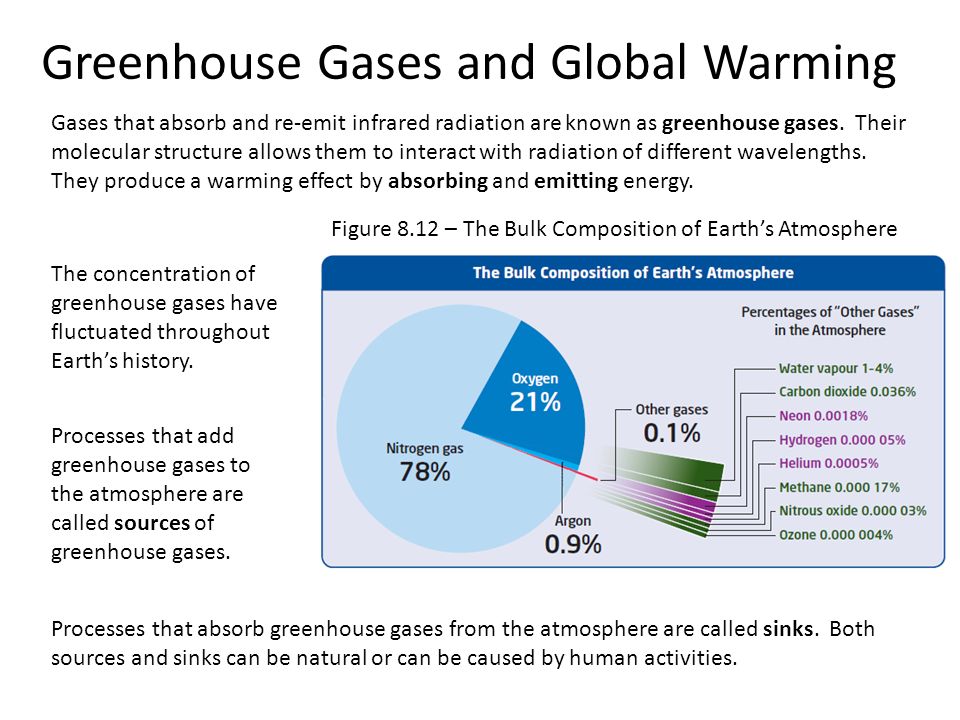



Greenhouse Gases And Human Activities Ppt Video Online Download
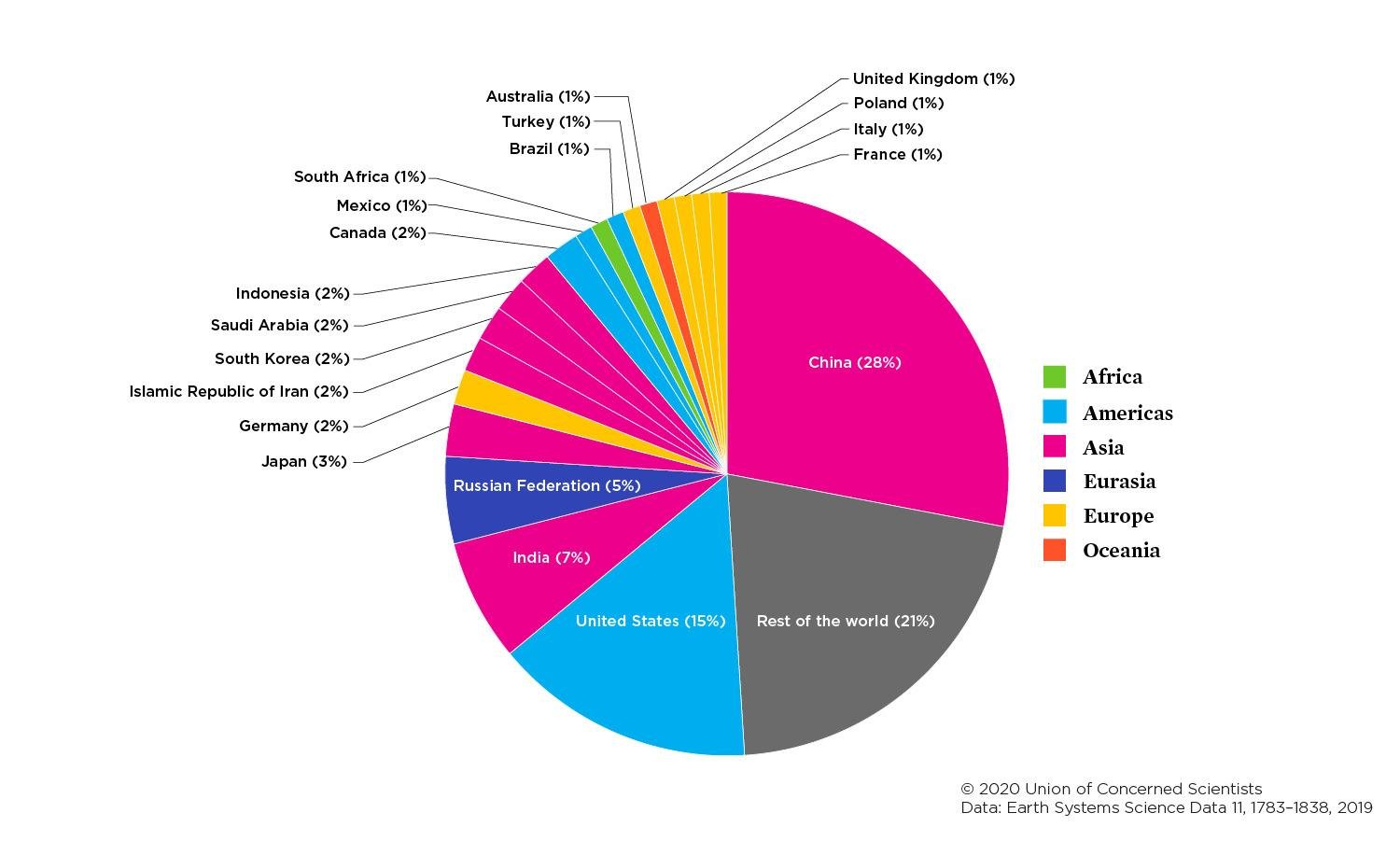



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists




Nea E2singapore Climate Change



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



Changes In Concentration Of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Other Greenhouse Gases And Aerosols




All Scenarios Assume Continued Growth In Atmospheric Levels Of Download Scientific Diagram




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Are Reduced How Quickly Do Their Concentrations In The Atmosphere Decrease Weadapt Climate Change Adaptation Planning Research And Practice
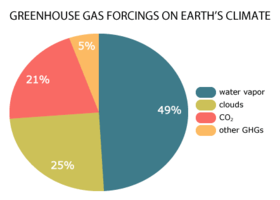



Which Are The Most Common Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Socratic




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Effect And Historical Emissions




What S In The Air Ucar Center For Science Education
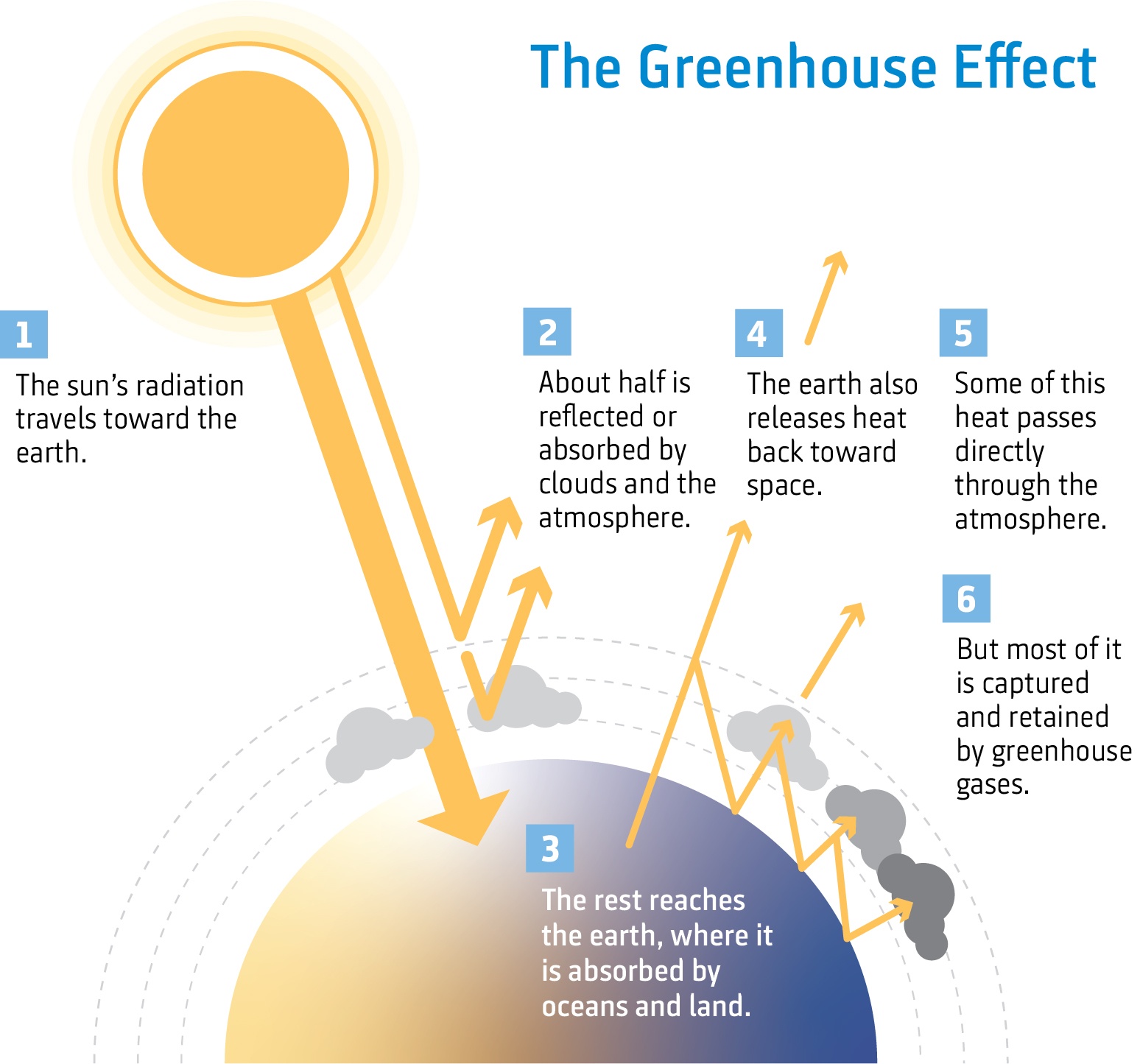



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Greenhouse Gases Climate Aware




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
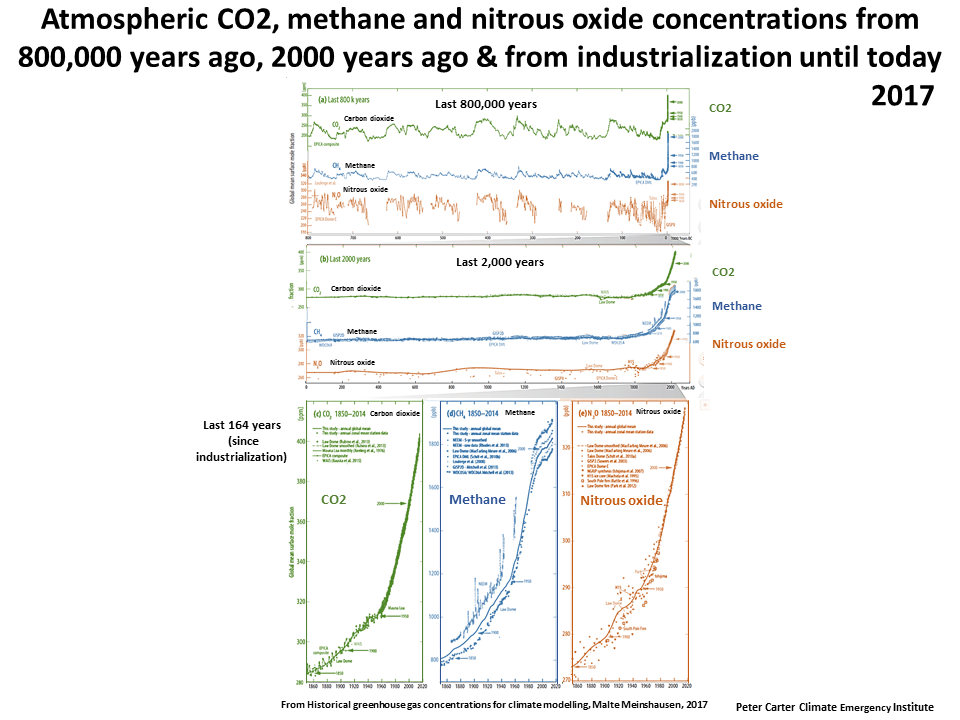



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gases



Who Are The Global Contributors Of Greenhouse Gases Understand The Cause And Reduce Global Warming
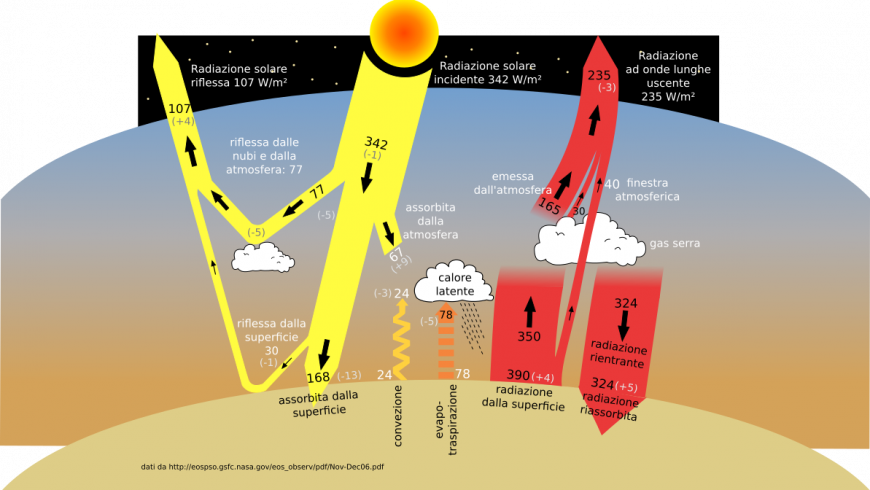



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions
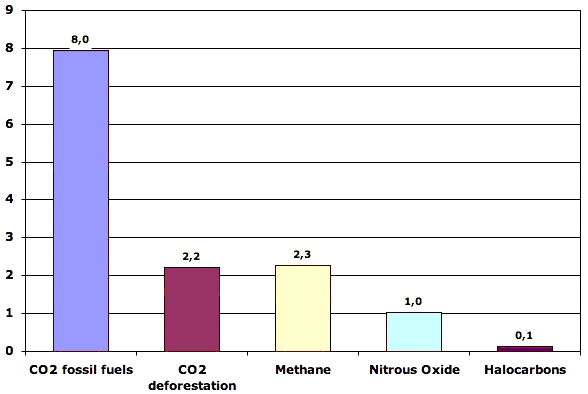



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
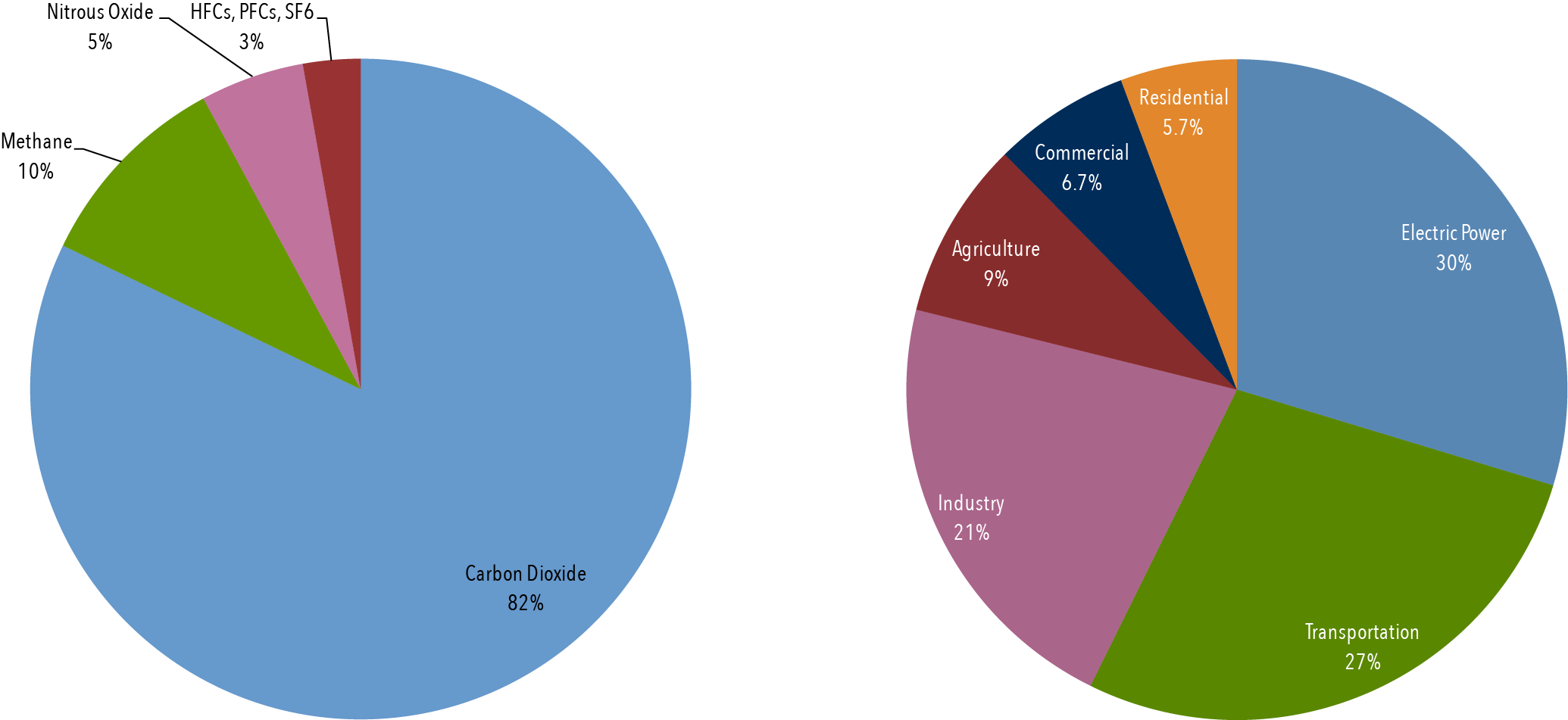



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



1
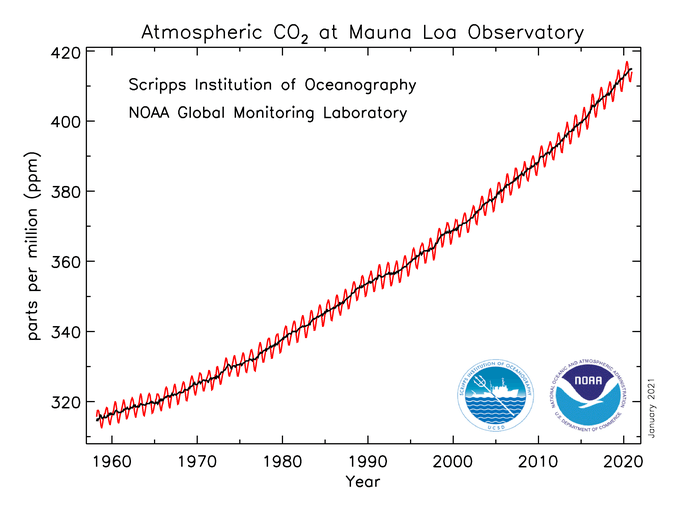



Main Greenhouse Gases Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record United Nations Sustainable Development



Climate Change Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Reduction Decarbonization Orkas
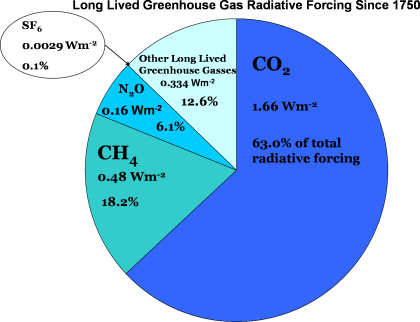



Noaa Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory



6 Major Types Of Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Atmosphere Wikiever
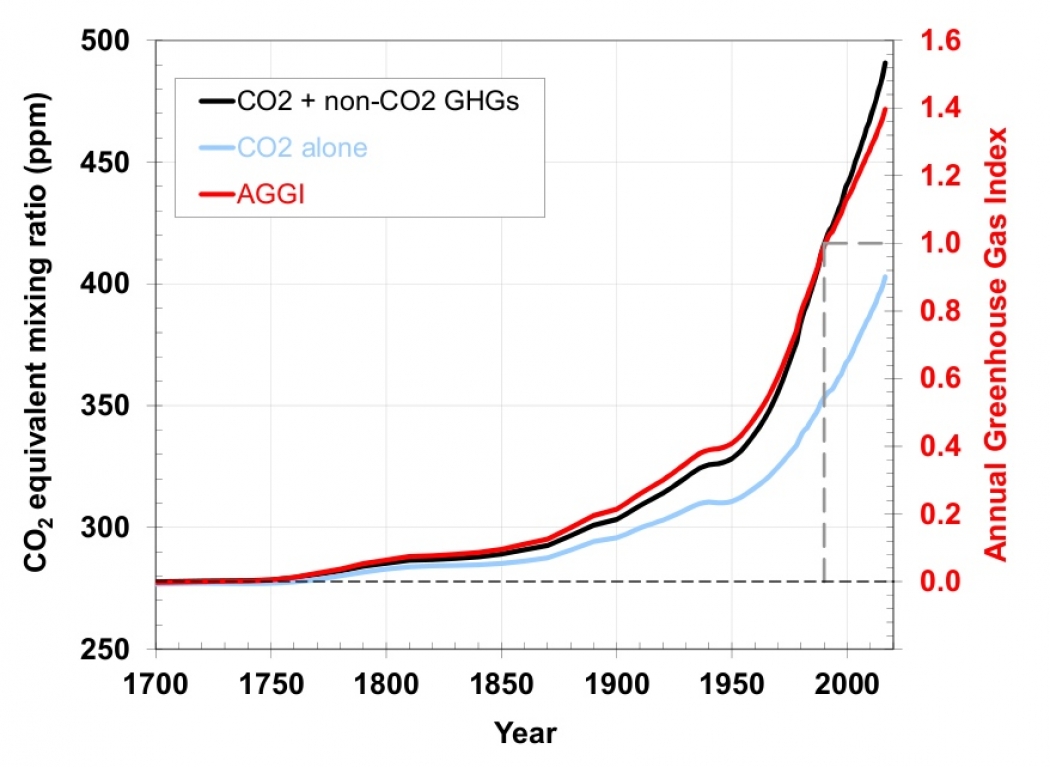



Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gases And The Atmosphere Science Learning Hub
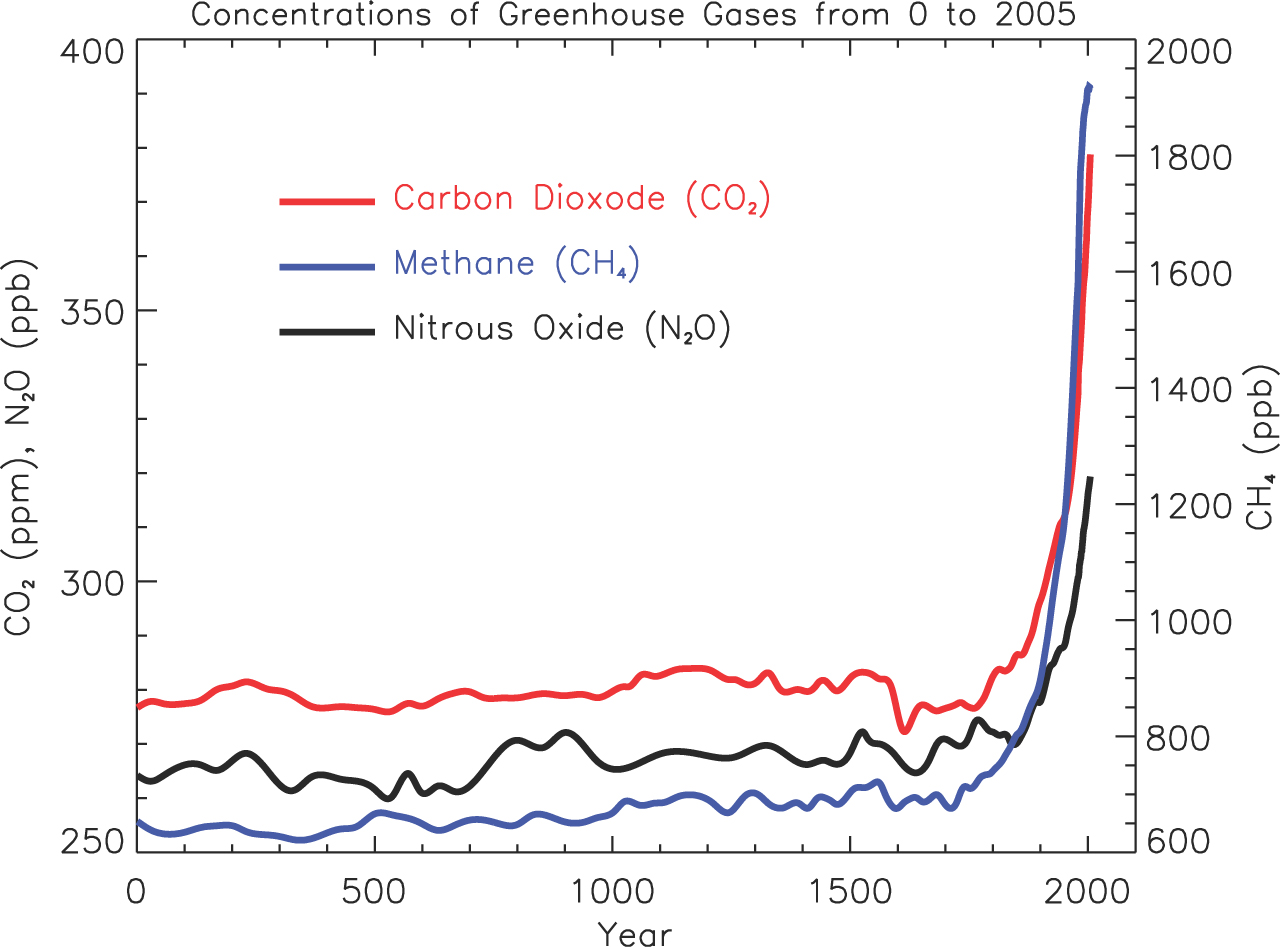



A World Of Images
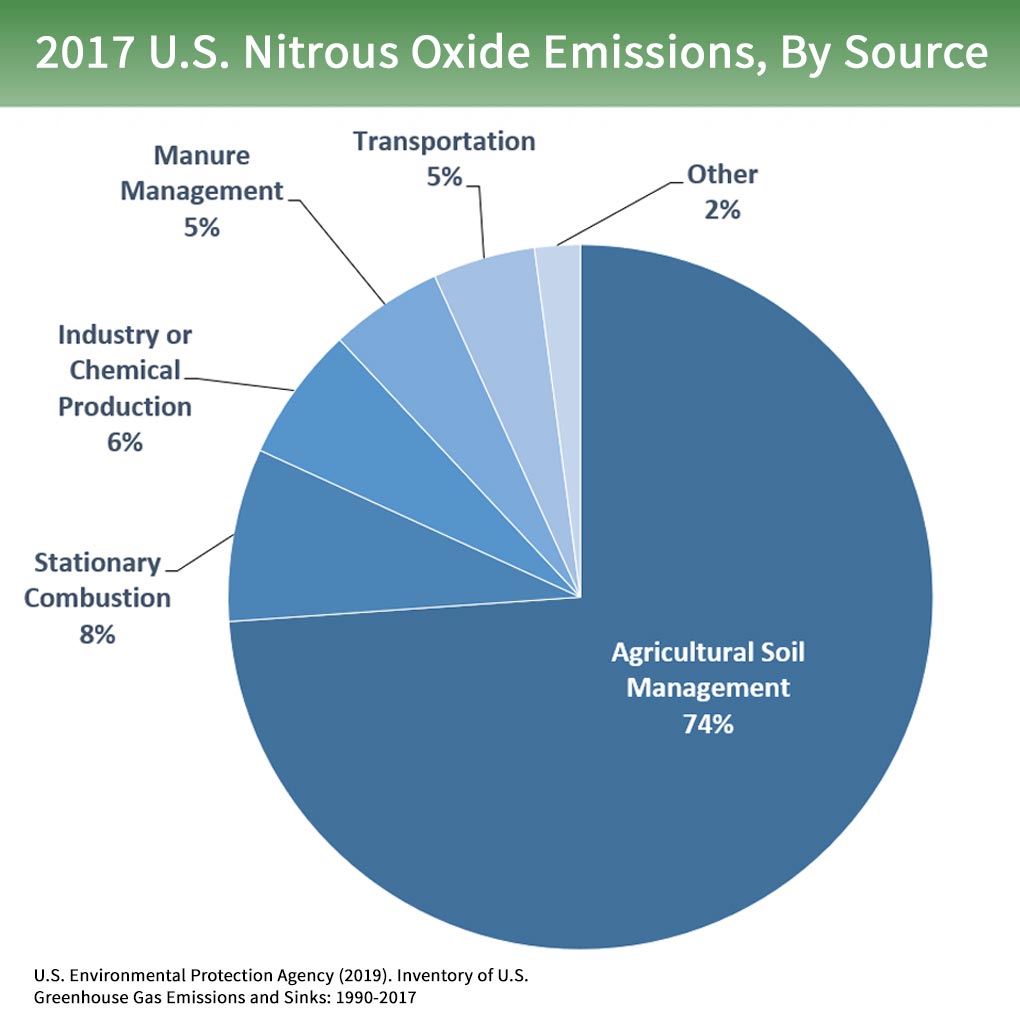



The Greenhouse Gas No One S Talking About Nitrous Oxide On Farms Explained Civil Eats



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
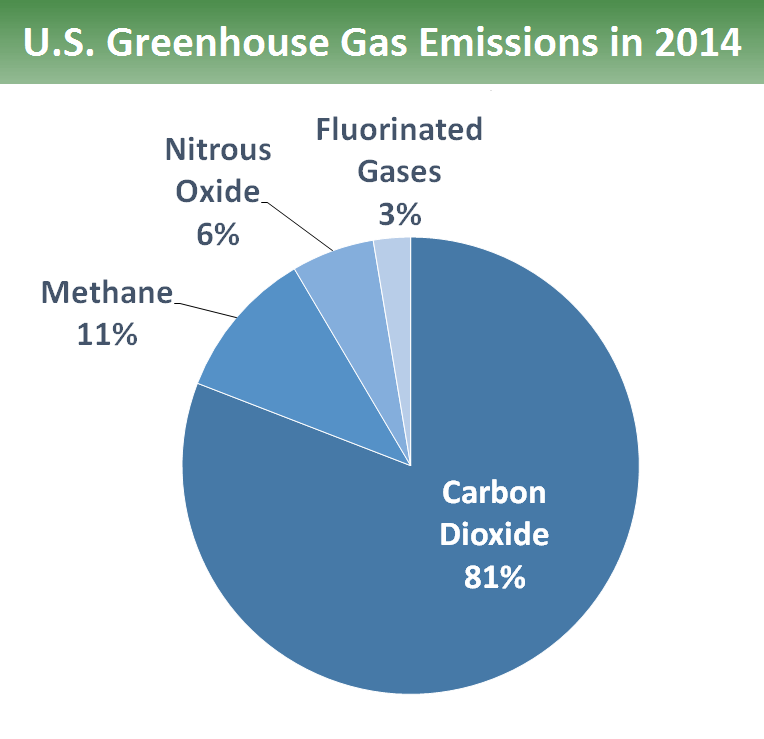



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




The Role Of Animal Agriculture On Greenhouse Gas Emissions




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Picture Talk



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿